How WISDEM works
Introduction
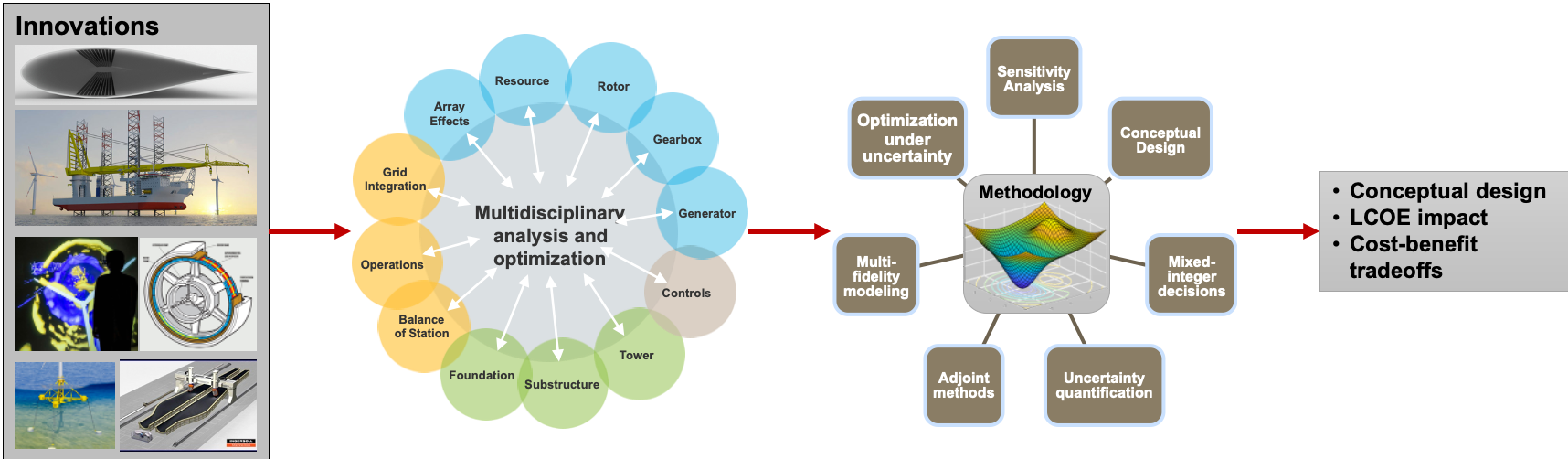
Full wind plants are comprised of multiple subsystems with varying degrees of technical complexity and many interfaces between many stakeholders. A systems engineering approach can transcend these subsystem boundaries and rigid interfaces to identify lower cost and higher performing designs that could not otherwise be achieved by focusing on individual components. The same approach also enables full system cost-benefit tradeoff and sensitivity studies when evaluating new component or logistical innovations. The Wind-plant Integrated System Design and Engineering Model (WISDEM) is an open-source software package that aims to meet these challenges and empower researcher to meet the following objects:
Apply multidisciplinary analysis and optimization (MDAO) to engineering and cost models in an open framework to enable full wind turbine and plant system analysis
Integrate technology or logistic innovations into the turbine and plant design through full system cost-benefit tradeoffs and sensitivity analyses
Promote collaborative research and analysis among national laboratories, industry, and academia
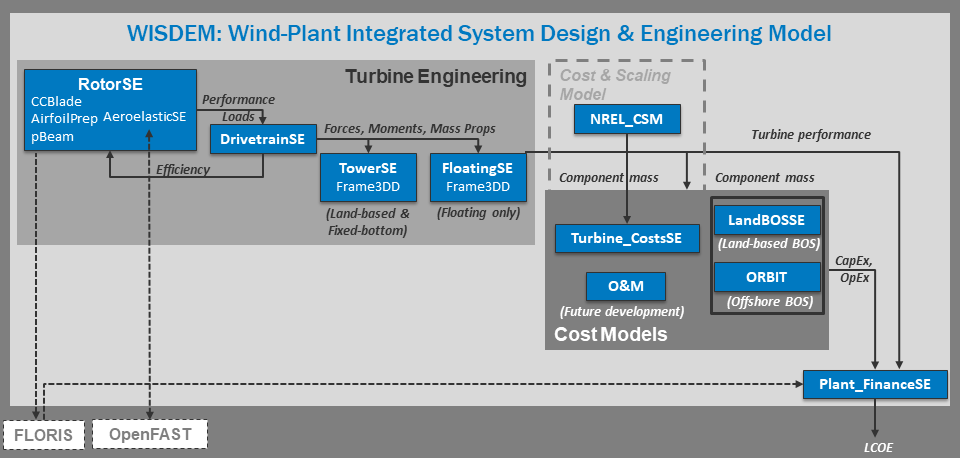
WISDEM is written in Python using OpenMDAO to manage data flow between analysis blocks and to specify the workflow when performing an analysis or optimization. WISDEM consists of a collection of physics and cost models for different components, at different fidelity levels, that can be combined together to answer system level research questions. All WISDEM models are steady-state and computational efficiency has always represented an important goal during the development of WISDEM to support wide explorations of the solution space.
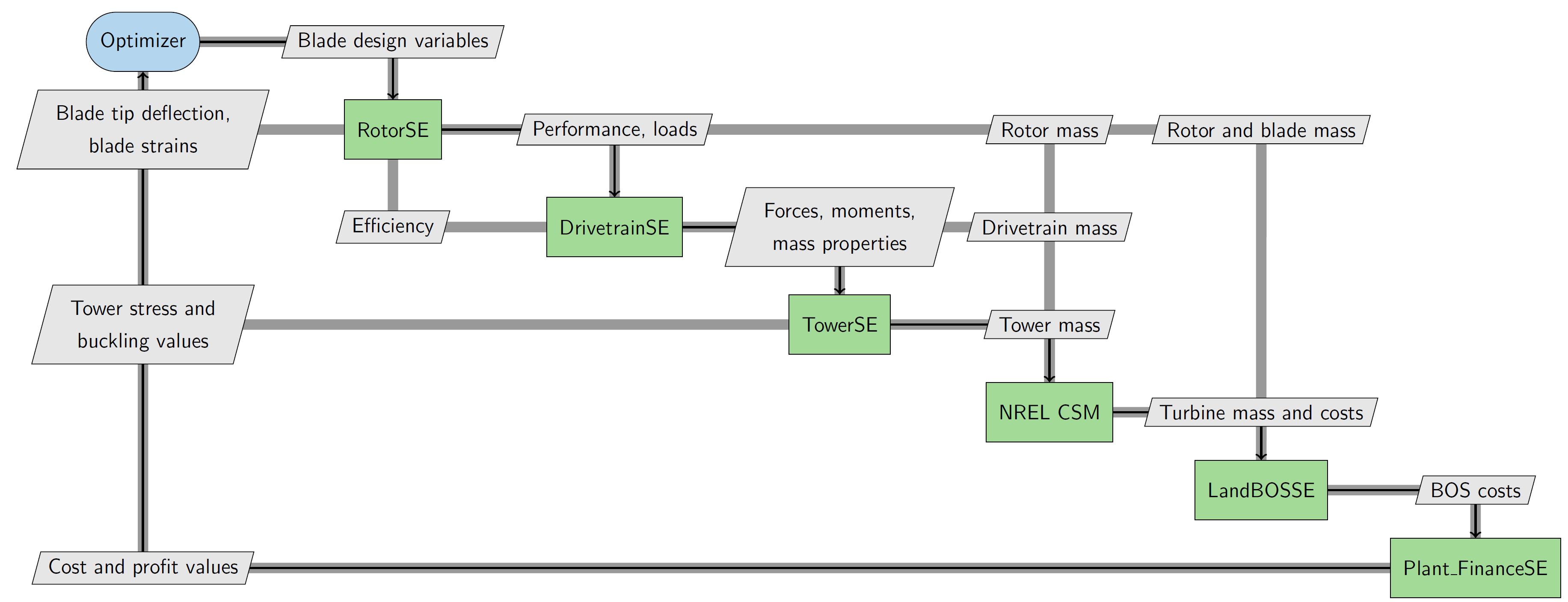
We’ve also provided an XDSM diagram showing how the WISDEM analysis blocks are connected. This diagram is based on the workflow for a turbine optimization where we vary blade design parameters.